Npm 5.5.1 Cannot Read Property 0 of Undefined
react-native-svg


react-native-svg provides SVG back up to React Native on iOS and Android, and a compatibility layer for the web.
Check out the demo
Looking for maintainers
https://github.com/react-native-svg/react-native-svg/bug/1554
Features
- Supports most SVG elements and properties (Rect, Circle, Line, Polyline, Polygon, 1000 ...).
- Easy to catechumen SVG code to react-native-svg.
- Installation
- Automatically
- Manually
- Android
- iOS
- Troubleshooting
- Opening issues
- Usage
- Use with content loaded from uri
- Apply with svg files
- Employ with xml strings
- Common props
- Supported elements
- Svg
- Rect
- Circle
- Ellipse
- Line
- Polygon
- Polyline
- Path
- Text
- TSpan
- TextPath
- G
- Utilize
- Symbol
- Defs
- Image
- ClipPath
- LinearGradient
- RadialGradient
- Mask
- Pattern
- Marking
- ForeignObject
- Bear upon Events
- Serialize
- Run example
- TODO
- Known issues
Installation
Automatically
With expo-cli
✅ The Expo client app comes with the native code installed!
Install the JavaScript with:
expo install react-native-svg
With react-native-cli
-
Install library
from npm
npm install react-native-svg
from yarn
yarn add together react-native-svg
-
Link native code
With autolinking (react-native 0.60+)
Pre 0.60
react-native link react-native-svg
NOTICE:
Due to breaking changes in react-native, the version given in the left column (and higher versions) of react-native-svg only supports the react-native version in the right column (and higher versions, if possible).
It is recommended to apply the version of react given in the peer dependencies of the react-native version you are using.
The latest version of react-native-svg should ever piece of work in a make clean react-native projection.
| react-native-svg | react-native |
|---|---|
| 3.ii.0 | 0.29 |
| four.2.0 | 0.32 |
| iv.3.0 | 0.33 |
| iv.4.0 | 0.38 |
| 4.v.0 | 0.xl |
| 5.1.8 | 0.44 |
| v.2.0 | 0.45 |
| v.3.0 | 0.46 |
| five.4.1 | 0.47 |
| v.5.1 | >=0.fifty |
| >=vi | >=0.50 |
| >=vii | >=0.57.4 |
| >=8 | >=0.57.4 |
| >=9 | >=0.57.4 |
Or, include this PR manually for v7+ stability on android for older RN ( included in 0.57-stable and newer).
The latest version of v6, v7, v8 and v9 should all piece of work in the latest react-native version.
v7 and newer requires the patch for making android thread safe, to get native animation support.
Manually
Android pre RN 0.60
-
yarn add react-native-svgIn RN 0.60+, this is all y'all should ever need to do get Android working. Before this, react-native link was responsible for the following steps: -
Append the following lines to
android/settings.gradle:include ':react-native-svg' project( ':react-native-svg' ).projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-svg/android' )
-
Insert the following lines within the dependencies block in
android/app/build.gradle:implementation project( ':react-native-svg' ) -
Open up
android/app/src/principal/java/[...]/MainApplication.java
- Add
import com.horcrux.svg.SvgPackage;to the imports at the top of the file - Add
new SvgPackage()to the list returned by thegetPackages()method. Add a comma to the previous item if in that location's already something there.
iOS pre RN 0.60
Manual linking
To install react-native-svg on iOS visit the link referenced above or exercise the following (react-native link should do this for you):
- Open your project in XCode and elevate the
RNSVG.xcodeprojfile (located in.../node_modules/react-native-svg/ios) into the Libraries directory shown in XCode. - Expand the
RNSVG.xcodeprojfile yous merely added to XCode until you run into:libRNSVG.a(located inRNSVG.xcodeproj>Products) - Drag
libRNSVG.ainto the Link Binary With Libraries department (located in Build Phases which may exist plant at the top of the XCode window)
CocoaPods
Alternatively, you tin can use CocoaPods to manage your native (Objective-C and Swift) dependencies:
- Add RNSVG to your Podfile (with RN 0.60+ autolinking, this is not needed)
pod 'RNSVG' , :path => '../node_modules/react-native-svg' If cocoapods is used and if error RNSVGImage.m:12:ix: 'React/RCTImageLoader.h' file not institute occurs:
Add the following entry in Podfile:
pod 'React' , :path => '../node_modules/react-native' , :subspecs => [ [...] 'RCTImage ' , # <-- Add RCTImage ] and run pod install from ios binder
Troubleshooting
Problems with Proguard
When Proguard is enabled (which it is by default for Android release builds), information technology causes runtime fault. To avoid this, add an exception to android/app/proguard-rules.pro:
-keep public course com.horcrux.svg.** {* ;} If you have build errors, and so it might be caused by caching problems, please try:
watchman watch-del-all rm -fr $TMPDIR/react-* react-native start --reset-cache Or, rm -rf node_modules yarn react-native start --reset-cache Unexpected beliefs
If y'all have unexpected beliefs, please create a make clean project with the latest versions of react-native and react-native-svg
react-native init CleanProject cd CleanProject/ yarn add together react-native-svg cd ios && pod install && cd .. Make a reproduction of the problem in App.js
react-native run-ios react-native run-android Opening issues
Verify that it is still an consequence with the latest version equally specified in the previous pace. If and then, open a new result, include the entire App.js file, specify what platforms y'all've tested, and the results of running this command:
If you doubtable that you've found a spec conformance bug, then you tin can exam using your component in a react-native-web project past forking this codesandbox, to see how different browsers return the same content: https://codesandbox.io/due south/pypn6mn3y7 If any evergreen browser with pregnant userbase or other svg user agent renders some svg content improve, or supports more of the svg and related specs, please open an upshot asap.
Usage
Hither'southward a simple example. To render output like this:
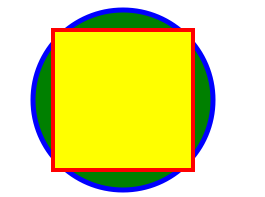
Use the post-obit lawmaking:
import Svg , { Circle , Ellipse , M , Text , TSpan , TextPath , Path , Polygon , Polyline , Line , Rect , Utilize , Prototype , Symbol , Defs , LinearGradient , RadialGradient , Finish , ClipPath , Pattern , Mask , } from 'react-native-svg' ; import React from 'react' ; import { View , StyleSheet } from 'react-native' ; export default class SvgExample extends React . Component { render ( ) { return ( < View style = { [ StyleSheet . absoluteFill , { alignItems: 'eye' , justifyContent: 'center' } , ] } > < Svg superlative = "50%" width = "50%" viewBox = "0 0 100 100" > < Circle cx = "l" cy = "50" r = "45" stroke = "bluish" strokeWidth = "2.five" fill = "green" / > < Rect ten = "xv" y = "15" width = "seventy" peak = "lxx" stroke = "red" strokeWidth = "2" make full = "yellow" / > < / Svg > < / View > ) ; } } Try this on Snack
Use with content loaded from uri
import * as React from 'react' ; import { SvgUri } from 'react-native-svg' ; export default ( ) => ( < SvgUri width = "100%" height = "100%" uri = "http://thenewcode.com/assets/images/thumbnails/homer-simpson.svg" / > ) ; CSS Support
If remote SVG file contains CSS in <way> element, use SvgCssUri:
import * every bit React from 'react' ; import { SvgCssUri } from 'react-native-svg' ; export default ( ) => ( < SvgCssUri width = "100%" peak = "100%" uri = "http://thenewcode.com/avails/svg/accessibility.svg" / > ) ; Utilise with svg files
Endeavour react-native-svg-transformer to get compile time conversion and buried transformations. https://github.com/kristerkari/react-native-svg-transformer#installation-and-configuration https://github.com/kristerkari/react-native-svg-transformer#for-react-native-v057-or-newer--expo-sdk-v3100-or-newer
metro.config.js
const { getDefaultConfig } = require ( 'metro-config' ) ; module . exports = ( async ( ) => { const { resolver: { sourceExts, assetExts } , } = expect getDefaultConfig ( ) ; return { transformer: { babelTransformerPath: require . resolve ( 'react-native-svg-transformer' ) , } , resolver: { assetExts: assetExts . filter ( ext => ext !== 'svg' ) , sourceExts: [...sourceExts , 'svg' ] , } , } ; } ) ( ) ; Import your .svg file within a React component:
import Logo from './logo.svg' ; Yous can then use your image equally a component:
< Logo width = { 120 } height = { 40 } / > Alternatively, you can use SvgXml with babel-plugin-inline-import, simply with transforms done at run-time.
.babelrc
{ "presets": [ "module:metro-react-native-babel-preset" ], "plugins": [ [ "boom-boom-plugin-inline-import" , { "extensions": [ ".svg" ] } ] ] } App.js
import * as React from 'react' ; import { SvgXml } from 'react-native-svg' ; import testSvg from './test.svg' ; export default ( ) => < SvgXml width = "200" height = "200" xml = { testSvg } / > ; Utilize with xml strings
import * every bit React from 'react' ; import { SvgXml } from 'react-native-svg' ; const xml = ` <svg width="32" height="32" viewBox="0 0 32 32"> <path fill-rule="evenodd" prune-dominion="evenodd" fill="url(#slope)" d="M4 0C1.79086 0 0 1.79086 0 4V28C0 30.2091 1.79086 32 4 32H28C30.2091 32 32 30.2091 32 28V4C32 ane.79086 thirty.2091 0 28 0H4ZM17 6C17 five.44772 17.4477 5 18 5H20C20.5523 5 21 5.44772 21 6V25C21 25.5523 20.5523 26 20 26H18C17.4477 26 17 25.5523 17 25V6ZM12 11C11.4477 11 11 11.4477 xi 12V25C11 25.5523 xi.4477 26 12 26H14C14.5523 26 15 25.5523 fifteen 25V12C15 eleven.4477 14.5523 11 14 11H12ZM6 18C5.44772 eighteen v 18.4477 5 19V25C5 25.5523 5.44772 26 6 26H8C8.55228 26 9 25.5523 nine 25V19C9 eighteen.4477 8.55228 18 8 18H6ZM24 14C23.4477 14 23 14.4477 23 15V25C23 25.5523 23.4477 26 24 26H26C26.5523 26 27 25.5523 27 25V15C27 xiv.4477 26.5523 14 26 14H24Z" /> <defs> <linearGradient id="gradient" x1="0" y1="0" x2="8.46631" y2="37.3364" gradient-units="userSpaceOnUse"> <end beginning="0" stop-color="#FEA267" /> <stop get-go="1" stop-color="#E75A4C" /> </linearGradient> </defs> </svg> ` ; consign default ( ) => < SvgXml xml = { xml } width = "100%" height = "100%" / > ; CSS support
If xml cord contains CSS in <style> element, use SvgCss:
import * every bit React from 'react' ; import { SvgCss } from 'react-native-svg' ; const xml = ` <svg width="32" height="32" viewBox="0 0 32 32"> <style> .red { fill: #ff0000; } </style> <rect class="red" x="0" y="0" width="32" summit="32" /> </svg> ` ; export default ( ) => < SvgCss xml = { xml } width = "100%" peak = "100%" / > ; Common props:
| Proper name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
| fill | '#000' | The fill up prop refers to the color inside the shape. |
| fillOpacity | 1 | This prop specifies the opacity of the colour or the content the current object is filled with. |
| fillRule | nonzero | The fillRule prop determines what side of a path is inside a shape, which determines how fill will paint the shape, can exist nonzero or evenodd |
| stroke | 'none' | The stroke prop controls how the outline of a shape appears. |
| strokeWidth | 1 | The strokeWidth prop specifies the width of the outline on the electric current object. |
| strokeOpacity | 1 | The strokeOpacity prop specifies the opacity of the outline on the current object. |
| strokeLinecap | 'square' | The strokeLinecap prop specifies the shape to be used at the stop of open subpaths when they are stroked. Can be either 'barrel', 'square' or 'round'. |
| strokeLinejoin | 'miter' | The strokeLinejoin prop specifies the shape to be used at the corners of paths or basic shapes when they are stroked. Can exist either 'miter', 'bevel' or 'round'. |
| strokeDasharray | [] | The strokeDasharray prop controls the pattern of dashes and gaps used to stroke paths. |
| strokeDashoffset | nix | The strokeDashoffset prop specifies the altitude into the dash blueprint to outset the nuance. |
| 10 | 0 | Translate altitude on x-axis. |
| y | 0 | Translate distance on y-axis. |
| rotation | 0 | Rotation degree value on the current object. |
| scale | 1 | Scale value on the current object. |
| origin | 0, 0 | Transform origin coordinates for the electric current object. |
| originX | 0 | Transform originX coordinates for the electric current object. |
| originY | 0 | Transform originY coordinates for the current object. |
Supported elements:
Svg
< Svg height = "100" width = "100" > < Rect x = "0" y = "0" width = "100" height = "100" fill up = "black" / > < Circumvolve cx = "50" cy = "50" r = "30" fill up = "yellow" / > < Circumvolve cx = "forty" cy = "40" r = "4" fill = "black" / > < Circle cx = "60" cy = "40" r = "4" fill = "black" / > < Path d = "M 40 60 A 10 10 0 0 0 sixty 60" stroke = "blackness" / > < / Svg > Colors gear up in the Svg element are inherited by its children:
< Svg width = "130" height = "130" fill up = "blueish" stroke = "cherry" color = "green" viewBox = "-16 -sixteen 544 544" > < Path d = "M318.37,85.45L422.53,190.11,158.89,455,54.79,350.38ZM501.56,lx.2L455.11,13.53a45.93,45.93,0,0,0-65.11,0L345.51,58.24,449.66,162.9l51.nine-52.15A35.8,35.8,0,0,0,501.56,sixty.2ZM0.29,497.49a11.88,xi.88,0,0,0,14.34,14.17l116.06-28.28L26.59,378.72Z" strokeWidth = "32" / > < Path d = "M0,0L512,512" stroke = "currentColor" strokeWidth = "32" / > < / Svg > 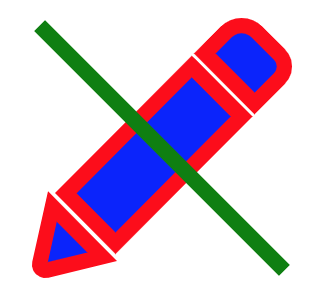
Code explanation:
- The fill prop defines the color within the object.
- The stroke prop defines the colour of the line drawn effectually the object.
- The colour prop is a bit special in the sense that it won't color anything by itself, only define a kind of color variable that can be used by children elements. In this example nosotros're defining a "green" color in the Svg element and using it in the 2nd Path element via stroke="currentColor". The "currentColor" is what refers to that "green" value, and it can be used in other props that accept colors too, due east.g. fill="currentColor".
Rect
The element is used to create a rectangle and variations of a rectangle shape:
< Svg width = "200" elevation = "60" > < Rect x = "25" y = "5" width = "150" summit = "50" fill = "rgb(0,0,255)" strokeWidth = "3" stroke = "rgb(0,0,0)" / > < / Svg > 
Code explanation:
- The width and acme props of the chemical element define the superlative and the width of the rectangle.
- The x prop defines the left position of the rectangle (e.g. x="25" places the rectangle 25 px from the left margin).
- The y prop defines the pinnacle position of the rectangle (due east.g. y="5" places the rectangle 5 px from the top margin).
Circumvolve
The chemical element is used to create a circle:
< Svg height = "100" width = "100" > < Circle cx = "fifty" cy = "50" r = "50" fill = "pinkish" / > < / Svg > 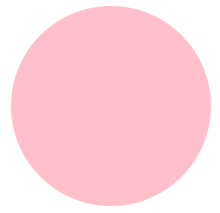
Lawmaking caption:
- The cx and cy props define the 10 and y coordinates of the center of the circle. If cx and cy are omitted, the circle's center is fix to (0,0)
- The r prop defines the radius of the circle
Ellipse
The element is used to create an ellipse.
An ellipse is closely related to a circle. The difference is that an ellipse has an x and a y radius that differs from each other, while a circle has equal x and y radius.
< Svg height = "100" width = "110" > < Ellipse cx = "55" cy = "55" rx = "50" ry = "thirty" stroke = "purple" strokeWidth = "2" fill up = "yellowish" / > < / Svg > 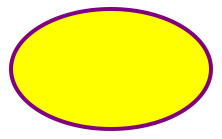
Code caption:
- The cx prop defines the 10 coordinate of the centre of the ellipse
- The cy prop defines the y coordinate of the centre of the ellipse
- The rx prop defines the horizontal radius
- The ry prop defines the vertical radius
Line
The element is an SVG bones shape, used to create a line connecting two points.
< Svg summit = "100" width = "100" > < Line x1 = "0" y1 = "0" x2 = "100" y2 = "100" stroke = "ruby-red" strokeWidth = "ii" / > < / Svg > 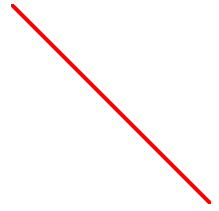
Code caption:
- The x1 prop defines the first of the line on the ten-axis.
- The y1 prop defines the start of the line on the y-axis.
- The x2 prop defines the end of the line on the 10-axis.
- The y2 prop defines the end of the line on the y-axis.
Polygon
The element is used to create a graphic that contains at least iii sides. Polygons are made of straight lines, and the shape is "airtight" (all the lines connect up).
< Svg height = "100" width = "100" > < Polygon points = "twoscore,5 70,eighty 25,95" fill = "lime" stroke = "purple" strokeWidth = "one" / > < / Svg > 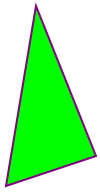
Lawmaking explanation:
- The points prop defines the x and y coordinates for each corner of the polygon
Polyline
The element is used to create any shape that consists of only straight lines:
< Svg height = "100" width = "100" > < Polyline points = "10,x 20,12 30,xx 40,60 60,seventy 95,ninety" fill = "none" stroke = "blackness" strokeWidth = "3" / > < / Svg > 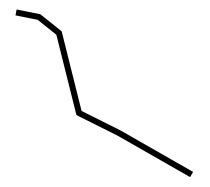
Lawmaking explanation:
- The points prop defines the x and y coordinates for each point of the polyline
Path
The element is used to define a path.
The following commands are available for path data:
- M = moveto
- L = lineto
- H = horizontal lineto
- 5 = vertical lineto
- C = curveto
- S = polish curveto
- Q = quadratic Bézier bend
- T = smoothen quadratic Bézier curveto
- A = elliptical Arc
- Z = closepath
Note: All of the commands above can too be expressed with lower letters. Majuscule letters means absolutely positioned, lower cases means relatively positioned. Come across Path document of SVG to know parameters for each command.
< Svg height = "100" width = "100" > < Path d = "M25 10 L98 65 L70 25 L16 77 L11 30 L0 4 L90 50 L50 10 L11 22 L77 95 L20 25" fill = "none" stroke = "blood-red" / > < / Svg > 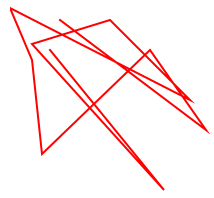
Text
The chemical element is used to ascertain text.
< Svg top = "60" width = "200" > < Text fill = "none" stroke = "purple" fontSize = "20" fontWeight = "bold" x = "100" y = "20" textAnchor = "centre" > STROKED TEXT < / Text > < / Svg > 
TSpan
The element is used to draw multiple lines of text in SVG. Rather than having to position each line of text absolutely, the element makes it possible to position a line of text relatively to the previous line of text.
< Svg meridian = "160" width = "200" > < Text y = "20" dx = "five v" > < TSpan 10 = "10" >tspan line ane< / TSpan > < TSpan ten = "10" dy = "fifteen" > tspan line 2 < / TSpan > < TSpan ten = "ten" dx = "x" dy = "15" > tspan line three < / TSpan > < / Text > < Text ten = "10" y = "60" make full = "red" fontSize = "14" > < TSpan dy = "5 10 20" >12345< / TSpan > < TSpan fill = "bluish" dy = "15" dx = "0 five 5" > < TSpan >6< / TSpan > < TSpan >7< / TSpan > < / TSpan > < TSpan dx = "0 ten 20" dy = "0 20" fontWeight = "bold" fontSize = "12" > 89a < / TSpan > < / Text > < Text y = "140" dx = "0 5 5" dy = "0 -v -5" > delta on text < / Text > < / Svg > 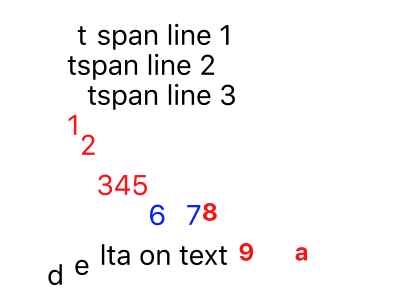
TextPath
In addition to text fatigued in a straight line, SVG also includes the power to identify text along the shape of a element. To specify that a block of text is to be rendered forth the shape of a , include the given text within a chemical element which includes an href aspect with a reference to a element.
< Svg height = "100" width = "200" > < Defs > < Path id = "path" d = { path } / > < / Defs > < G y = "20" > < Text fill = "blue" > < TextPath href = "#path" startOffset = "-10%" > We go upward and downwards, < TSpan fill = "carmine" dy = "5,5,5" > then up again < / TSpan > < / TextPath > < / Text > < Path d = { path } make full = "none" stroke = "cherry-red" strokeWidth = "one" / > < / Grand > < / Svg > 
G
The chemical element is a container used to group other SVG elements. Transformations applied to the g chemical element are performed on all of its child elements, and whatsoever of its props are inherited past its child elements. It can too group multiple elements to be referenced later with the <Utilize /> element.
< Svg height = "100" width = "200" > < G rotation = "50" origin = "100, 50" > < Line x1 = "lx" y1 = "ten" x2 = "140" y2 = "10" stroke = "#060" / > < Rect 10 = "60" y = "20" height = "50" width = "80" stroke = "#060" fill = "#060" / > < Text x = "100" y = "75" stroke = "#600" fill = "#600" textAnchor = "middle" > Text grouped with shapes < / Text > < / Yard > < / Svg > 
Use
The element can reuse an SVG shape from elsewhere in the SVG document, including elements and elements. The reused shape can be defined inside the <Defs> chemical element (which makes the shape invisible until used) or outside.
< Svg height = "100" width = "300" > < Defs > < G id = "shape" > < G > < Circle cx = "l" cy = "50" r = "l" / > < Rect x = "l" y = "50" width = "50" meridian = "fifty" / > < Circle cx = "50" cy = "50" r = "5" fill up = "bluish" / > < / G > < / Thou > < / Defs > < Use href = "#shape" x = "20" y = "0" / > < Employ href = "#shape" 10 = "170" y = "0" / > < / Svg > This example shows a element divers inside a <Defs> element. This makes the invisible unless referenced past a element.
Before the element can be referenced, it must have an ID assail it via its id prop. The element references the chemical element via its href prop. Notice the # in front of the ID in the prop value.
The element specifies where to show the reused shapes via its ten and y props. Notice that the shapes inside the element are located at 0,0. That is done because their position is added to the position specified in the element.

Symbol
The SVG chemical element is used to ascertain reusable symbols. The shapes nested inside a are not displayed unless referenced by a chemical element.
< Svg height = "150" width = "110" > < Symbol id = "symbol" viewBox = "0 0 150 110" width = "100" height = "50" > < Circle cx = "50" cy = "50" r = "40" strokeWidth = "8" stroke = "carmine" make full = "red" / > < Circle cx = "90" cy = "60" r = "xl" strokeWidth = "eight" stroke = "dark-green" make full = "white" / > < / Symbol > < Apply href = "#symbol" x = "0" y = "0" / > < Use href = "#symbol" x = "0" y = "l" width = "75" top = "38" / > < Use href = "#symbol" x = "0" y = "100" width = "50" pinnacle = "25" / > < / Svg > 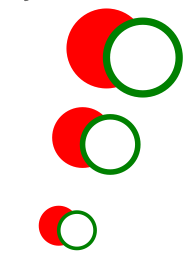
Defs
The element is used to embed definitions that can exist reused inside an SVG image. For instance, you can group SVG shapes together and reuse them as a single shape.
Image
The element allows a raster image to be included in an Svg component.
< Svg height = "100" width = "100" > < Defs > < ClipPath id = "clip" > < Circumvolve cx = "50%" cy = "fifty%" r = "xl%" / > < / ClipPath > < / Defs > < Rect x = "0" y = "0" width = "100%" height = "100%" fill = "cherry-red" / > < Rect ten = "5%" y = "v%" width = "50%" pinnacle = "90%" / > < Image ten = "5%" y = "five%" width = "fifty%" meridian = "90%" preserveAspectRatio = "xMidYMid slice" opacity = "0.five" href = { crave ( '../epitome.jpg' ) } clipPath = "url(#clip)" / > < Text x = "50" y = "fifty" textAnchor = "eye" fontWeight = "bold" fontSize = "sixteen" fill = "blue" > HOGWARTS < / Text > < / Svg > 
ClipPath
The SVG element defines a clipping path. A clipping path is used/referenced using the clipPath belongings
< Svg pinnacle = "100" width = "100" > < Defs > < RadialGradient id = "grad" cx = "50%" cy = "50%" rx = "l%" ry = "l%" fx = "l%" fy = "50%" gradientUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" > < Terminate offset = "0%" stopColor = "#ff0" stopOpacity = "1" / > < Stop outset = "100%" stopColor = "#00f" stopOpacity = "ane" / > < / RadialGradient > < ClipPath id = "clip" > < 1000 scale = "0.9" x = "10" > < Circle cx = "30" cy = "30" r = "20" / > < Ellipse cx = "60" cy = "seventy" rx = "20" ry = "ten" / > < Rect x = "65" y = "15" width = "30" elevation = "xxx" / > < Polygon points = "20,60 twenty,lxxx l,70" / > < Text x = "50" y = "30" fontSize = "32" fontWeight = "bold" textAnchor = "middle" scale = "1.2" > Q < / Text > < / Grand > < / ClipPath > < / Defs > < Rect x = "0" y = "0" width = "100" top = "100" fill = "url(#grad)" clipPath = "url(#clip)" / > < / Svg > 
LinearGradient
The element is used to define a linear gradient. The element must be nested within a <Defs> tag. The <Defs> tag is short for definitions and contains definition of special elements (such as gradients).
Linear gradients tin can be divers as horizontal, vertical or athwart gradients:
- Horizontal gradients are created when y1 and y2 are equal and x1 and x2 differ
- Vertical gradients are created when x1 and x2 are equal and y1 and y2 differ
- Angular gradients are created when x1 and x2 differ and y1 and y2 differ
< Svg height = "150" width = "300" > < Defs > < LinearGradient id = "grad" x1 = "0" y1 = "0" x2 = "1" y2 = "0" > < Stop commencement = "0" stopColor = "#FFD080" stopOpacity = "one" / > < Stop offset = "1" stopColor = "red" stopOpacity = "ane" / > < / LinearGradient > < / Defs > < Ellipse cx = "150" cy = "75" rx = "85" ry = "55" fill up = "url(#grad)" / > < / Svg > Code explanation:
- The id prop of the tag defines a unique name for the slope
- The x1, x2, y1,y2 props of the tag define the start and stop position of the gradient
- The color range for a gradient tin be equanimous of ii or more colors. Each color is specified with a tag. The starting time prop is used to define where the gradient color brainstorm and stop
- The fill up prop links the ellipse element to the gradient
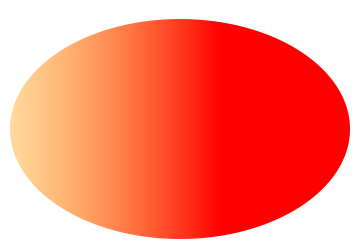
NOTICE: LinearGradient too supports percentage equally prop:
< LinearGradient id = "grad" x1 = "0%" y1 = "0%" x2 = "100%" y2 = "0%" > < Cease first = "0%" stopColor = "rgb(255,255,0)" stopOpacity = "0" / > < Finish offset = "100%" stopColor = "red" stopOpacity = "1" / > < / LinearGradient > This result is same every bit the example earlier. Only information technology'southward recommend to apply exact number instead; it has operation advantages over using percentages.
RadialGradient
The element is used to define a radial gradient. The chemical element must exist nested within a <Defs> tag. The <Defs> tag is short for definitions and contains definition of special elements (such as gradients).
< Svg top = "150" width = "300" > < Defs > < RadialGradient id = "grad" cx = "150" cy = "75" rx = "85" ry = "55" fx = "150" fy = "75" gradientUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" > < Finish outset = "0" stopColor = "#ff0" stopOpacity = "i" / > < Stop offset = "ane" stopColor = "#83a" stopOpacity = "ane" / > < / RadialGradient > < / Defs > < Ellipse cx = "150" cy = "75" rx = "85" ry = "55" make full = "url(#grad)" / > < / Svg > Code explanation:
- The id prop of the tag defines a unique name for the gradient
- The cx, cy and r props define the outermost circumvolve and the fx and fy define the innermost circle
- The colour range for a slope tin can be composed of 2 or more colors. Each color is specified with a tag. The offset prop is used to define where the gradient colour begin and terminate
- The fill prop links the ellipse chemical element to the gradient

Mask
In SVG, you can specify that whatever other graphics object or 'One thousand' element can be used equally an blastoff mask for compositing the electric current object into the background.
A mask is defined with a 'Mask' element. A mask is used/referenced using the 'mask' property.
A 'Mask' can contain whatsoever graphical elements or container elements such equally a 'G'.
The chemical element must be nested inside a <Defs> tag. The <Defs> tag is short for definitions and contains definition of special elements (such as gradients).
https://world wide web.w3.org/TR/SVG11/images/masking/mask01.svg
< Svg width = "100%" height = "100%" viewBox = "0 0 800 300" > < Defs > < LinearGradient id = "Gradient" gradientUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" x1 = "0" y1 = "0" x2 = "800" y2 = "0" > < Finish offset = "0" stopColor = "white" stopOpacity = "0" / > < Terminate showtime = "one" stopColor = "white" stopOpacity = "i" / > < / LinearGradient > < Mask id = "Mask" maskUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" x = "0" y = "0" width = "800" meridian = "300" > < Rect x = "0" y = "0" width = "800" meridian = "300" fill = "url(#Slope)" / > < / Mask > < Text id = "Text" ten = "400" y = "200" fontFamily = "Verdana" fontSize = "100" textAnchor = "eye" > Masked text < / Text > < / Defs > < Rect x = "0" y = "0" width = "800" meridian = "300" fill = "#FF8080" / > < Use href = "#Text" make full = "blue" mask = "url(#Mask)" / > < Use href = "#Text" fill = "none" stroke = "black" stroke-width = "ii" / > < / Svg > Code explanation: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/masking.html#MaskElement

v10 adds experimental support for using masks together with native elements. If you lot had native elements inside any Svg root before (which was unsupported), Then your content might change appearance when upgrading, every bit east.g. transforms and masks now take effect.
Pattern
A pattern is used to fill or stroke an object using a pre-defined graphic object which can exist replicated ("tiled") at stock-still intervals in ten and y to cover the areas to be painted. Patterns are divers using a 'pattern' element and so referenced by properties 'fill' and 'stroke' on a given graphics chemical element to indicate that the given chemical element shall be filled or stroked with the referenced blueprint. The element must be nested within a <Defs> tag. The <Defs> tag is short for definitions and contains definition of special elements (such as gradients).
https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/images/pservers/pattern01.svg
< Svg width = "100%" height = "100%" viewBox = "0 0 800 400" > < Defs > < Blueprint id = "TrianglePattern" patternUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" x = "0" y = "0" width = "100" height = "100" viewBox = "0 0 10 10" > < Path d = "M 0 0 L vii 0 L 3.5 seven z" fill = "red" stroke = "bluish" / > < / Blueprint > < / Defs > < Rect fill up = "none" stroke = "blue" x = "ane" y = "1" width = "798" meridian = "398" / > < Ellipse fill = "url(#TrianglePattern)" stroke = "blackness" strokeWidth = "5" cx = "400" cy = "200" rx = "350" ry = "150" / > < / Svg > Code caption: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/pservers.html#PatternElement

Marker
A marker is a symbol which is attached to one or more than vertices of 'path', 'line', 'polyline' and 'polygon' elements. Typically, markers are used to make arrowheads or polymarkers. Arrowheads can be divers past attaching a marker to the start or terminate vertices of 'path', 'line' or 'polyline' elements. Polymarkers can exist defined by attaching a mark to all vertices of a 'path', 'line', 'polyline' or 'polygon' chemical element.
The graphics for a mark are divers past a 'mark' element. To indicate that a particular 'marker' element should be rendered at the vertices of a particular 'path', 'line', 'polyline' or 'polygon' element, set up one or more marking properties ('marker', 'marker-showtime', 'marker-mid' or 'marker-end') to reference the given 'marker' chemical element.
https://world wide web.w3.org/TR/SVG11/images/painting/mark.svg
< Svg width = "400" height = "200" viewBox = "0 0 4000 2000" > < Defs > < Marking id = "Triangle" viewBox = "0 0 10 x" refX = "0" refY = "five" markerUnits = "strokeWidth" markerWidth = "iv" markerHeight = "three" orient = "auto" > < Path d = "Grand 0 0 L x five Fifty 0 10 z" / > < / Mark > < / Defs > < Rect ten = "10" y = "10" width = "3980" height = "1980" fill = "none" stroke = "bluish" strokeWidth = "10" / > < Path d = "Grand 1000 750 L 2000 750 L 2500 1250" fill = "none" stroke = "black" strokeWidth = "100" markerEnd = "url(#Triangle)" / > < / Svg > Lawmaking explanation: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG11/painting.html#Markers

import React from 'react' ; import { StyleSheet , View } from 'react-native' ; import { SvgXml } from 'react-native-svg' ; const markerRendering = `<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="275" height="200" viewBox="0 0 100 30"> <defs> <marker id="m1" viewBox="0 0 10 x" refX="5" refY="5" markerWidth="8" markerHeight="8"> <circle cx="five" cy="5" r="5" fill="green"/> </marker> <marker id="m2" viewBox="0 0 10 10" refX="five" refY="5" markerWidth="6.5" markerHeight="6.5"> <circumvolve cx="v" cy="v" r="5" fill up="skyblue" opacity="0.nine"/> </marker> <marker id="m3" viewBox="0 0 10 ten" refX="five" refY="5" markerWidth="5" markerHeight="5"> <circle cx="v" cy="five" r="5" fill="maroon" opacity="0.85"/> </marker> </defs> <path d="M10,10 h10 v10 z m20,0 h10 v10 z m20,0 h10 v10 z" make full="none" stroke="black" marker-first="url(#m1)" marker-mid="url(#m2)" marker-stop="url(#m3)" /> </svg>` ; export default form App extends React . Component { render ( ) { return ( < View fashion = { styles . container } > < SvgXml xml = { markerRendering } / > < / View > ) ; } } const styles = StyleSheet . create ( { container: { backgroundColor: 'white' , justifyContent: 'center' , alignItems: 'center' , flex: 1 , } , } ) ; 
import React from 'react' ; import { StyleSheet , View } from 'react-native' ; import { SvgXml } from 'react-native-svg' ; const markerRendering = `<svg xmlns="http://world wide web.w3.org/2000/svg" width="275" acme="200" viewBox="0 0 275 200"> <defs> <marker id="Triangle" viewBox="0 0 10 10" refX="1" refY="5" markerUnits="strokeWidth" markerWidth="four" markerHeight="3" orient="auto"> <path d="Thousand 0 0 Fifty 10 five Fifty 0 x z" fill="context-stroke" /> </marking> </defs> <g make full="none" stroke-width="10" marker-end="url(#Triangle)"> <path stroke="crimson" d="Thou 100,75 C 125,fifty 150,50 175,75" marker-end="url(#Triangle)"/> <path stroke="olivedrab" d="K 175,125 C 150,150 125,150 100,125" marker-end="url(#Triangle)"/> </thousand> </svg>` ; export default course App extends React . Component { render ( ) { return ( < View fashion = { styles . container } > < SvgXml xml = { markerRendering } / > < / View > ) ; } } const styles = StyleSheet . create ( { container: { backgroundColor: 'white' , justifyContent: 'eye' , alignItems: 'center' , flex: ane , } , } ) ; 
Code explanation: https://www.w3.org/TR/SVG2/painting.html#VertexMarkerProperties
ForeignObject
SVG is designed to be compatible with other XML languages for describing and rendering other types of content. The 'foreignObject' element allows for inclusion of elements in a non-SVG namespace which is rendered within a region of the SVG graphic using other user agent processes. The included foreign graphical content is subject to SVG transformations, filters, clipping, masking and compositing.
One goal for SVG is to provide a mechanism by which other XML language processors tin can render into an area within an SVG drawing, with those renderings subject area to the diverse transformations and compositing parameters that are currently active at a given point inside the SVG content tree. One particular example of this is to provide a frame for XML content styled with CSS or XSL and so that dynamically reflowing text (bailiwick to SVG transformations and compositing) could be inserted into the middle of some SVG content.
https://svgwg.org/svg2-draft/embedded.html#ForeignObjectElement https://world wide web.w3.org/TR/SVG11/extend.html#ForeignObjectElement
import React , { Component } from 'react' ; import { Text , View , Image } from 'react-native' ; import { Svg , Defs , LinearGradient , Stop , Mask , Rect , G , Circumvolve , ForeignObject , } from 'react-native-svg' ; export default grade App extends Component { return ( ) { return ( < View style = { { flex: 1 , justifyContent: 'centre' } } > < Svg height = "50%" > < Defs > < LinearGradient id = "Slope" gradientUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" x1 = "0" y1 = "0" x2 = "800" y2 = "0" > < End kickoff = "0" stopColor = "white" stopOpacity = "0.2" / > < Finish offset = "1" stopColor = "white" stopOpacity = "1" / > < / LinearGradient > < Mask id = "Mask" maskUnits = "userSpaceOnUse" x = "0" y = "0" width = "800" meridian = "300" > < Rect 10 = "0" y = "0" width = "800" height = "300" fill = "url(#Gradient)" / > < / Mask > < / Defs > < G mask = "url(#Mask)" > < Circle cx = { 50 } cy = { 70 } r = { 65 } / > < ForeignObject ten = { 50 } y = { 0 } width = { 100 } height = { 100 } > < View mode = { { width: 200 , height: 400 , transform: [ ] } } > < Paradigm style = { { width: 200 , pinnacle: 200 } } source = { { uri: 'https://picsum.photos/200/200' , } } / > < / View > < / ForeignObject > < ForeignObject 10 = { 55 } y = { 5 } width = { 100 } superlative = { 100 } > < View style = { { width: 200 , height: 400 , transform: [ ] } } > < Text style = { { colour: 'blue' } } >Testing< / Text > < Text manner = { { color: 'green' } } >Testing2< / Text > < / View > < / ForeignObject > < / Yard > < / Svg > < / View > ) ; } } Touch Events
Touch events are supported in react-native-svg. These include:
-
disabled -
onPress -
onPressIn -
onPressOut -
onLongPress -
delayPressIn -
delayPressOut -
delayLongPress
Yous can use these events to provide interactivity to your react-native-svg components.
< Circle cx = "l%" cy = "50%" r = "38%" make full = "red" onPress = { ( ) => alert ( 'Press on Circle' ) } / > 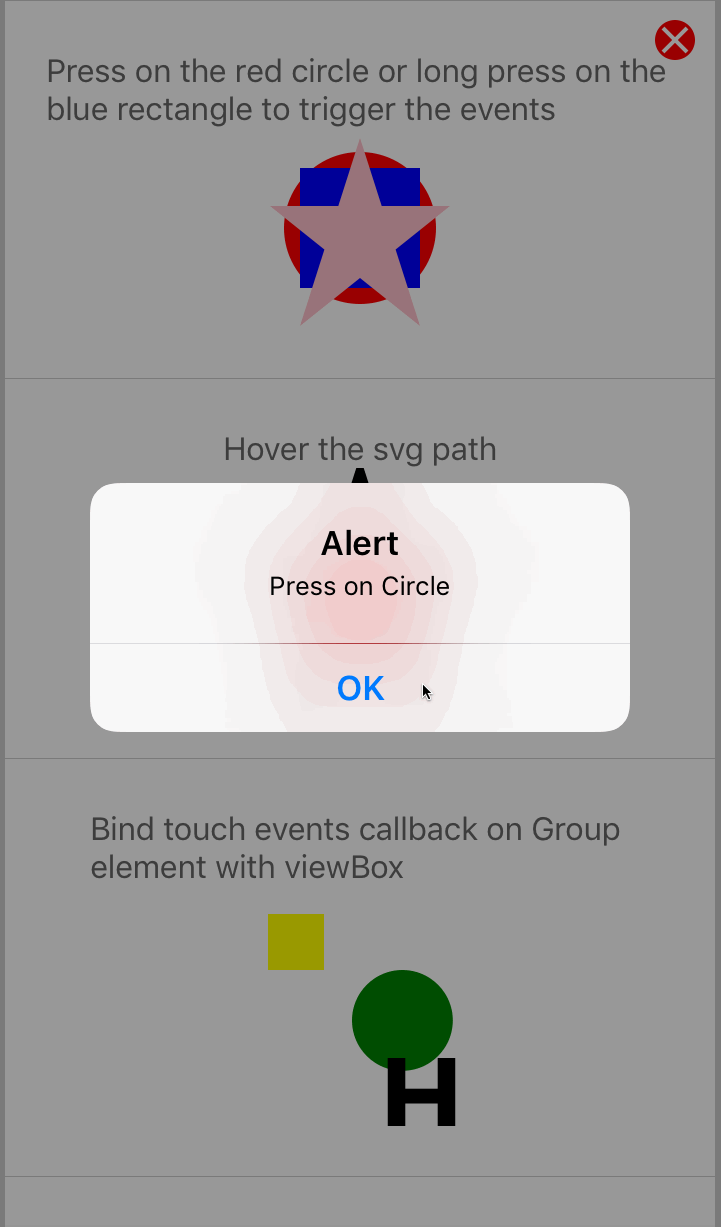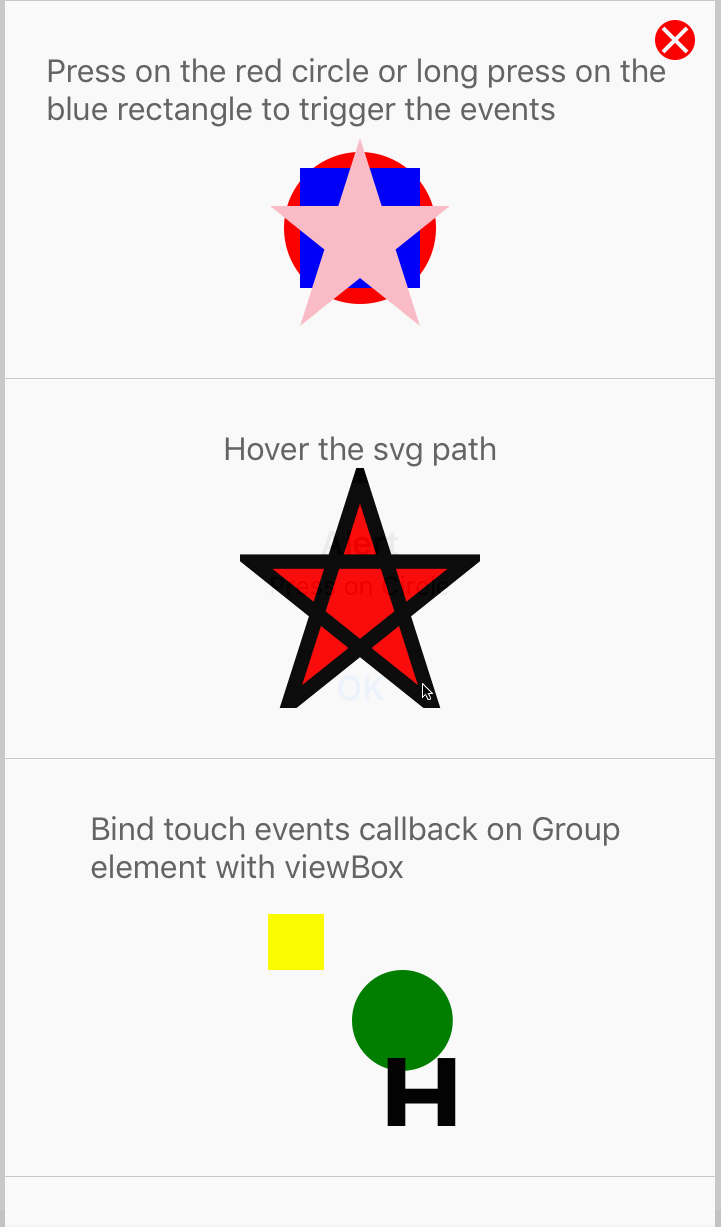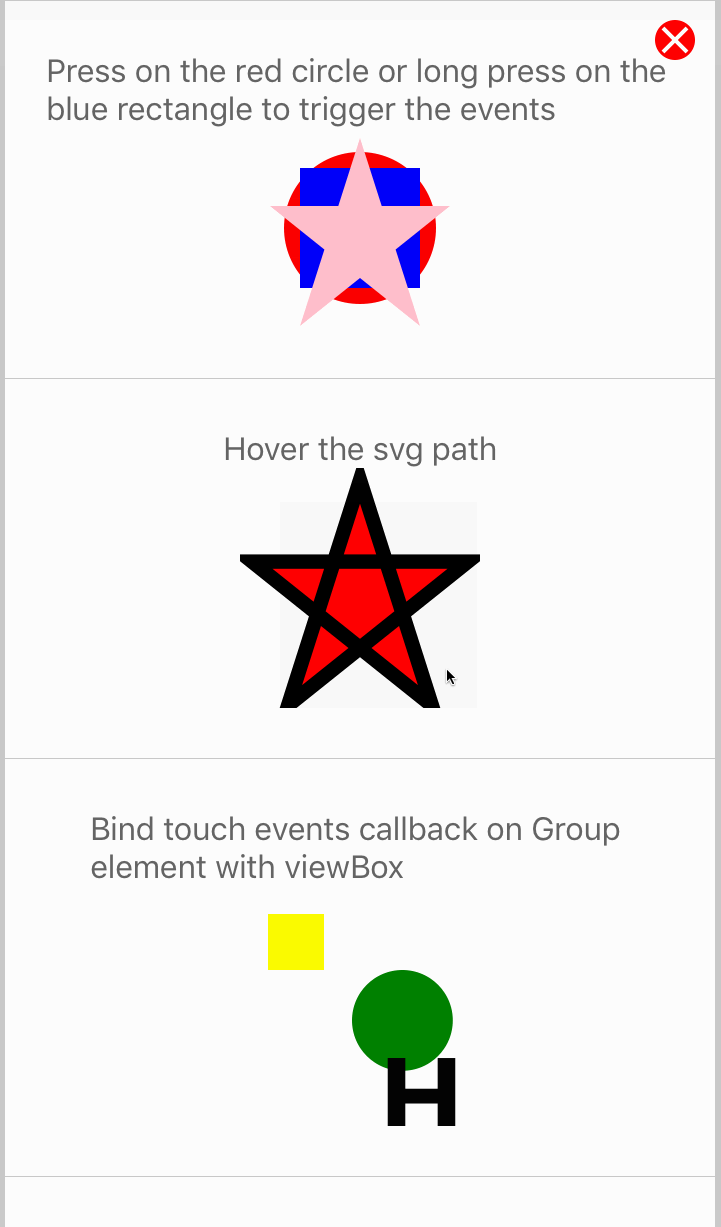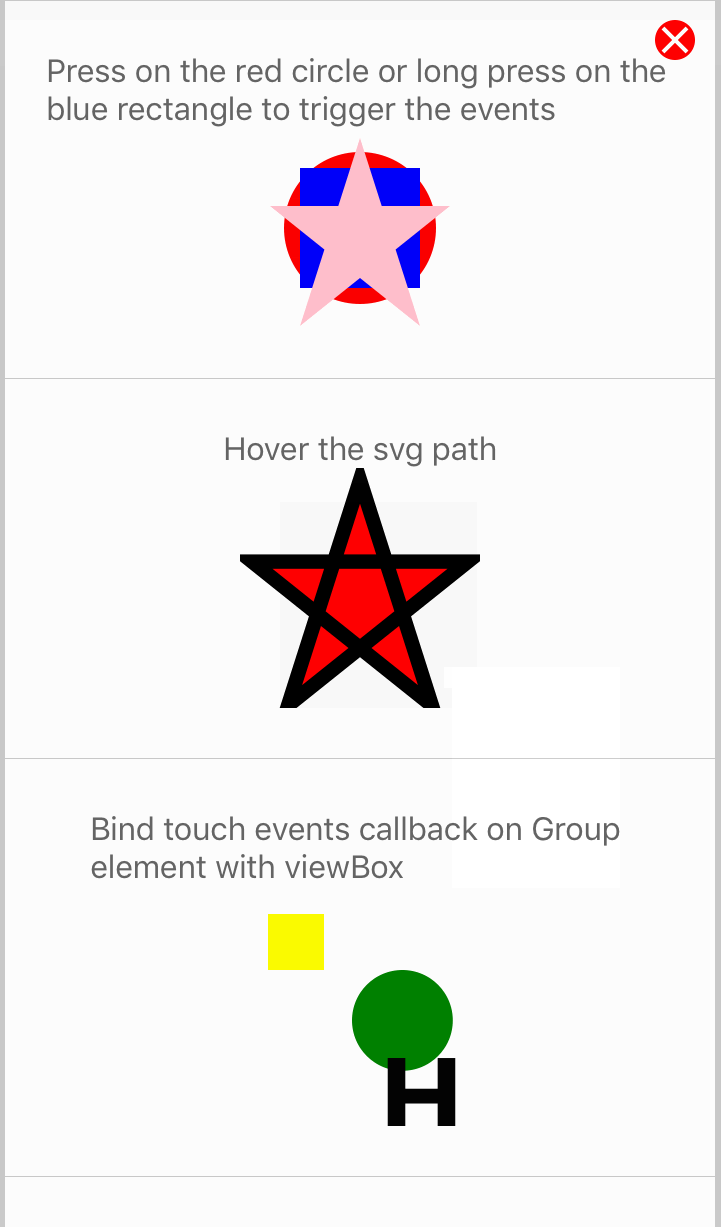
For more examples of bear upon in activity, checkout the TouchEvents.js examples.
Serialize
import * as React from 'react' ; import { Platform , StyleSheet , TouchableOpacity } from 'react-native' ; import { Svg , Rect } from 'react-native-svg' ; import ReactDOMServer from 'react-dom/server' ; const isWeb = Platform . OS === 'spider web' ; const childToWeb = child => { const { blazon, props } = child ; const proper name = type && type . displayName ; const webName = proper noun && proper name [ 0 ] . toLowerCase ( ) + name . piece ( 1 ) ; const Tag = webName ? webName : type ; return < Tag {...props } > { toWeb ( props . children ) } < / Tag > ; } ; const toWeb = children => React . Children . map ( children , childToWeb ) ; consign default class App extends React . Component { renderSvg ( ) { return ( < Svg tiptop = "100%" width = "100%" style = { { backgroundColor: '#33AAFF' } } > < Rect x = "l" y = "50" width = "50" pinnacle = "50" fill = "#3399ff" strokeWidth = "3" stroke = "rgb(0,0,0)" / > < / Svg > ) ; } serialize = ( ) => { const element = this . renderSvg ( ) ; const webJsx = isWeb ? element : toWeb ( element ) ; const svgString = ReactDOMServer . renderToStaticMarkup ( webJsx ) ; console . log ( svgString ) ; } ; render ( ) { return ( < TouchableOpacity manner = { styles . container } onPress = { this . serialize } > { this . renderSvg ( ) } < / TouchableOpacity > ) ; } } const styles = StyleSheet . create ( { container: { flex: 1 , justifyContent: 'center' , backgroundColor: '#ecf0f1' , padding: 8 , } , } ) ; Run example:
git clone https://github.com/magicismight/react-native-svg-example.git cd react-native-svg-example yarn # run Android: react-native run-android # run iOS: react-native run-ios TODO:
- Filters
Known bug:
- Unable to apply focus signal of RadialGradient on Android.
johnsonhistogives.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.npmjs.com/package/react-native-svg
0 Response to "Npm 5.5.1 Cannot Read Property 0 of Undefined"
Publicar un comentario